Antarctic Ice Shelves Show Signs of Increased Melting
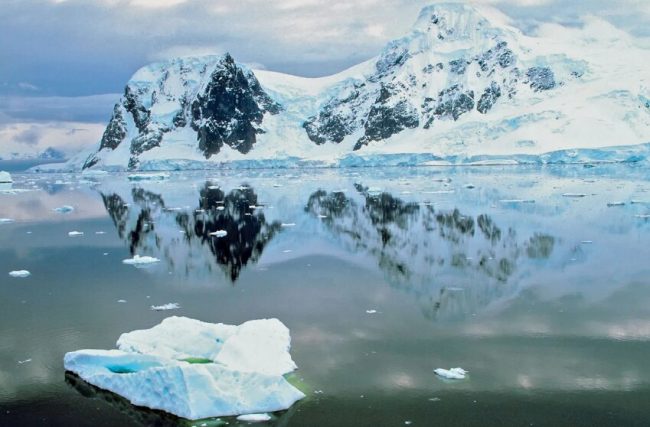

Antarctica is a vast, icy continent located at the Earth’s South Pole. It’s one of the most remote and inhospitable places on Earth, yet it continues to be a subject of scientific interest
Climate Change: Antarctica is experiencing the effects of climate change, with rising temperatures leading to melting glaciers and ice shelves. This has significant implications for sea level rise and global weather patterns.
Scientific Research: Scientists continue to conduct research in Antarctica, studying topics such as climate change, biodiversity, and the history of the Earth. Tourism: While tourism to Antarctica is strictly regulated, it has been increasing in recent years, raising concerns about its impact on the fragile environment.
Geopolitical Issues: Antarctica is a unique region with no permanent residents. Its governance is governed by the Antarctic Treaty, which prohibits military
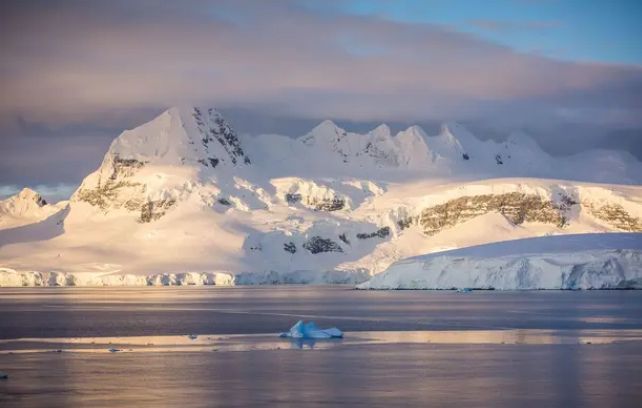

Scientists studying Antarctica have reported alarming signs of accelerated ice shelf melting in recent months. The ice shelves, which act as barriers holding back glaciers from sliding into the ocean, are thinning due to rising global temperatures.
A research team based in the western Antarctic region observed cracks forming more rapidly than in previous years. The melting of these ice shelves could contribute to significant sea level rise, threatening coastal communities around the globe.
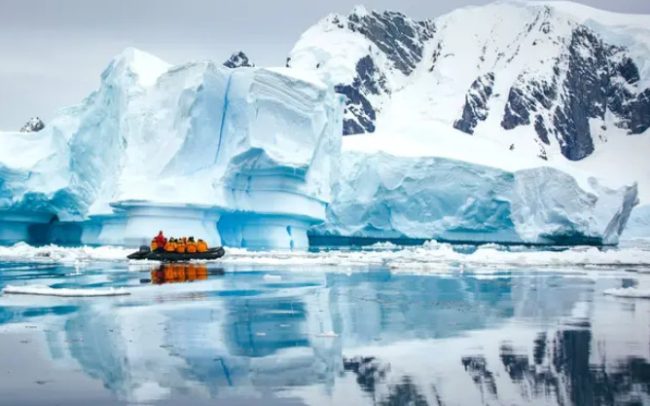

Experts are calling for immediate international cooperation to mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Without swift action, the delicate balance of Antarctica’s ecosystem may be irreversibly damaged, leading to long-term consequences for the planet.
